Getting a better view of the retina for earlier detection and better control of disorders
Up until recently the best an optometrist or ophthalmologist could achieve with a handheld indirect ophthalmoscope was a limited view of your retina (fundus) after full dilation of your pupils. If associated with other problems of the lens media like cataracts this view was limited still further. Now there is a collection of new technology available that can improve that view and spot symptoms and disorders (retinopathies) of the retina earlier. These disorders often occur at the outer edge of the retina (ora serrata), towards the front of the eye behind the Iris and could often not be seen by older methods easily.
These machines are very expensive given the technology involved and could not be entertained by the fees received by optometrists for an NHS sight test. (less than £20) as they also take more clinic time as well as leasing or purchase costs. However patients with no known problems only need an eye examination every 2 years, and those with suspect conditions will need checks more often. Depending on the machine involved and the number of procedures necessary, the costs will be an additional £20 to £100. Less than keeping your car MOT’d and serviced, so what’s more important?
Let’s begin with improving the images seen of the retina using the Optomap:
The Optomap panoramic retinal scanner
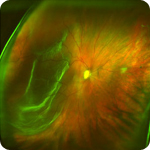
Retinal DetachmentThis produces a laser scan of the whole of the eye’s retina, producing a high-definition, multicolour image and in most cases the 200 degree sweep of the retina does not require dilation of the pupil and it can actually see past the densest of cataracts. Because the images are digital they can be saved for future comparison year on year, sent for further evaluation to other experts and even printed for your own saving.
Scans can show the earliest signs of a detached retina, retinal holes, macular degeneration, and high blood pressure. This is because the retina is the only place one can see blood running within the arteries, veins and arterioles and so twisted arteries tend to show high blood pressure, leaky vessels and new growth of vessels are prevalent in diabetes as well as renal conditions, and clots of cholesterol could indicate a possibility of stroke related conditions. This is a painless procedure with only a short period of after image being apparent.
The Optomap® is provided by Optos.
And there are a variety of other fundus camera systems provided:
Digital retinal photography
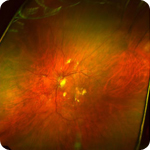
These provide a high-resolution, digital photograph of the central 30 degrees of the retina, the important part that includes the optic disc (where the optic nerve joins the retina) and the fovea (the central part of the macula, the most sensitive part of the retina).
Similar to the Optomap but with less of a sweep of the retina they are useful for detecting diabetes, macular degeneration, and optic nerve problems.
Now let’s go one leap forward to imaging the retina in cross section
The Optical Coherence Tomography Scanner (OCT)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) uses light waves to create detailed images of underlying retinal structures. Using this scanner, we can more specifically diagnose, treat and manage glaucoma and retinal diseases including diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration.
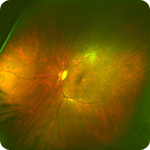
The retina consists of many layers of different tissues each providing a different function to enable the rods and cones to be stimulated by light, that means good nourishment from cells, a method of waste removal and the passage of the light stimulus through the nerve system.
A lack of nourishment, or a separation of the layers caused by bleeding or new blood vessel growth will create blind spots in the retina and if unchecked eventual blindness. In the same way if a build up occurs in waste products made by the photo cells then these will become defective. Retinal bleeds are created by a number of diseases as well as age related disorders thought to be linked to free radicals within the retina.
New treatments for wet AMD using Lucentis and for diabetic bleeds using Avastin are now being used under the NICE procedures agreement and these are having dramatic effects on saving and in many cases improving vision.
The OCT gives a dramatic cross sectional image of the retina scanning through the 200 degrees of retina and holes or schisms within the layers can be pinpointed and treated by these new drugs or by laser or photo dynamic procedures.
In summary
• The advanced OCT technology provides detailed images of the retina not observable by any other means.
• This non-contact, non-invasive equipment can provide earlier confirmation of damage so treatment can be started earlier and with greater knowledge
• Continuing medication can be assessed for success and the dosage can be changed to suit the progression. This is important when Lucentis injections cost around £750 per shot.
• The scanner produces high-resolution (10 times greater resolution than any other technique available), cross-sectional images of the retina.
• This equipment does not require injections or exposure to painful, high-intensity light, which means improved patient comfort and safety.
OCTs are made by Topcon, Humphreys and Zeiss, Heidelberg and others .



















